Overview
This October I chose to partake in the NASA Space Apps Challenge, a 2-day hackathon dedicated to solving problems related to space and earth exploration. My group chose to tackle the "InSAR change detectives" problem, trying to eliminate atmospheric water vapor interference from satellite readings. I was solely responsible for designing the algorithm, implementing the code in a Python Jupyter Notebook, and creating a presentation and team page for our group's submission. Run on Google Colab here or view on GitHub over here
Design
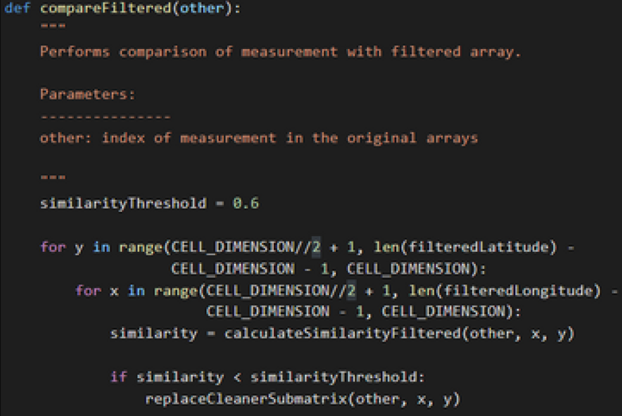
- Imported, processed, and graphed satellite NetCDF4 data using NumPy, Matplotlib, and other libraries
- Quantified the difference between successive readings by computing the cosine similarity of corresponding areas and comparing statistical coherence values
Results
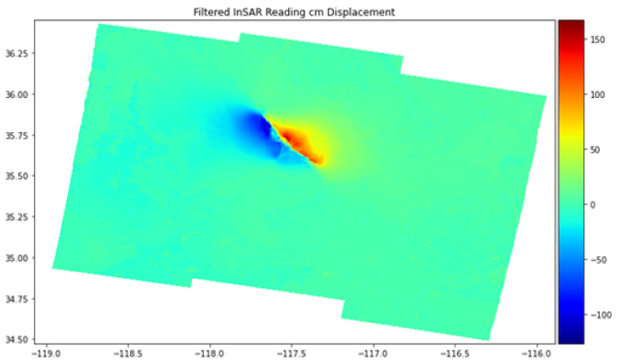
- Filters and stitches together multiple readings without blurring or distorting InSAR data
- Statistical filter can be applied to all sorts of noise affecting satellite signals
- Successfully applied algorithm to eight readings from the Ridgecrest 2019 earthquake event